Understanding the "Water Pump" Category
The term "water pump" encompasses any device engineered to displace water from one location to another, typically by creating pressure or suction. This category includes a variety of pumping mechanisms, each suited for different applications and water conditions. Examples of other types of water pumps include:
-
Positive Displacement Pumps: These pumps move a fixed amount of fluid with each cycle. Examples include piston pumps, diaphragm pumps, and rotary lobe pumps. They are often used for high-pressure, low-flow applications or for handling viscous fluids, though some are specifically designed for water (e.g., hand pumps for wells).
-
Submersible Pumps: While many submersible pumps are centrifugal in design, the term "submersible" refers to their ability to be fully immersed in the fluid they are pumping.
-
Jet Pumps: These pumps use an ejector to create a vacuum, drawing water from a well.
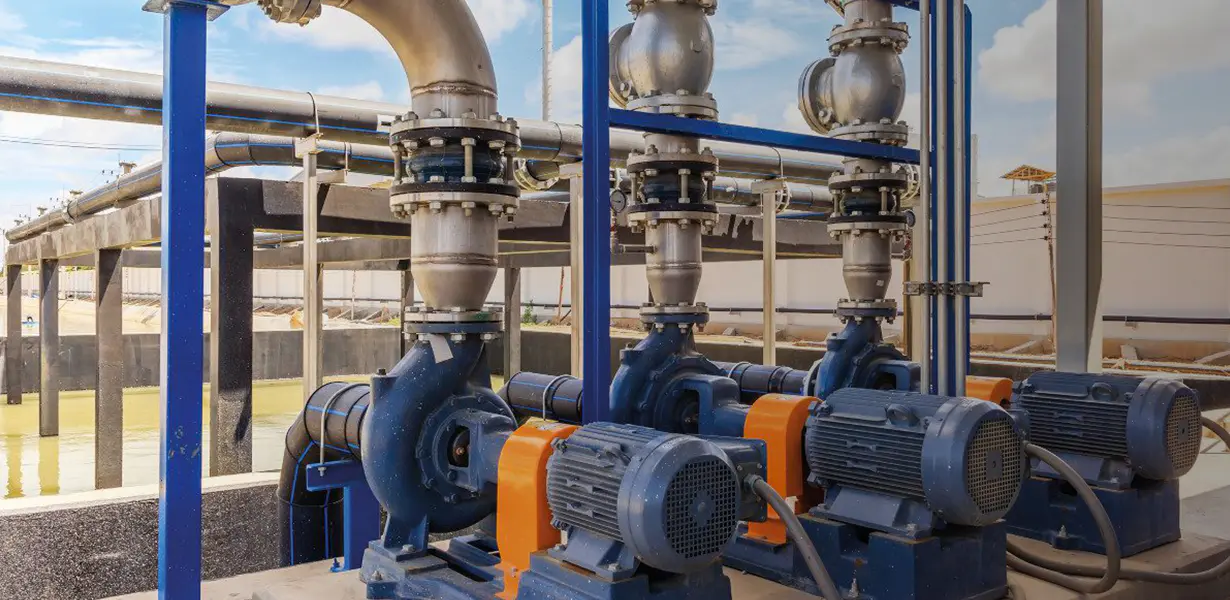
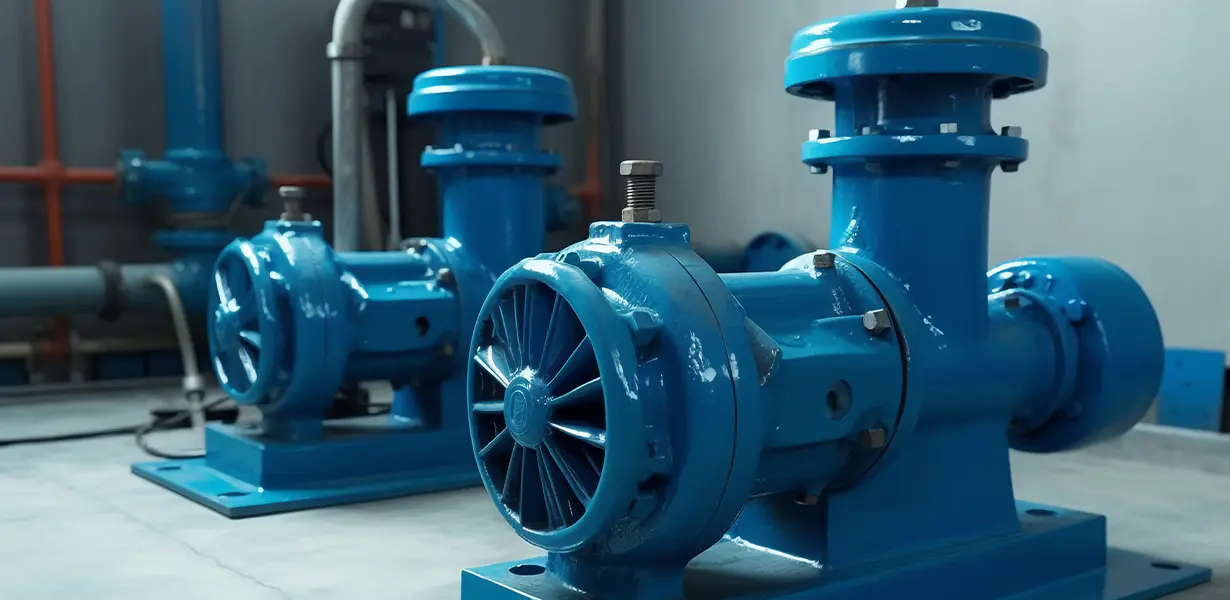
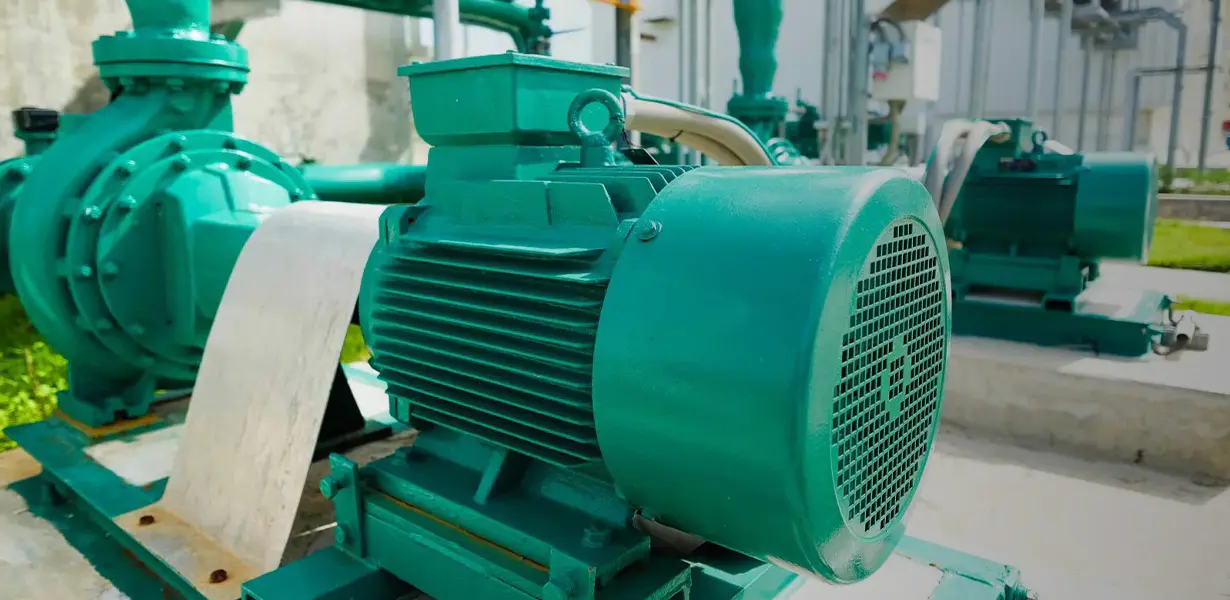
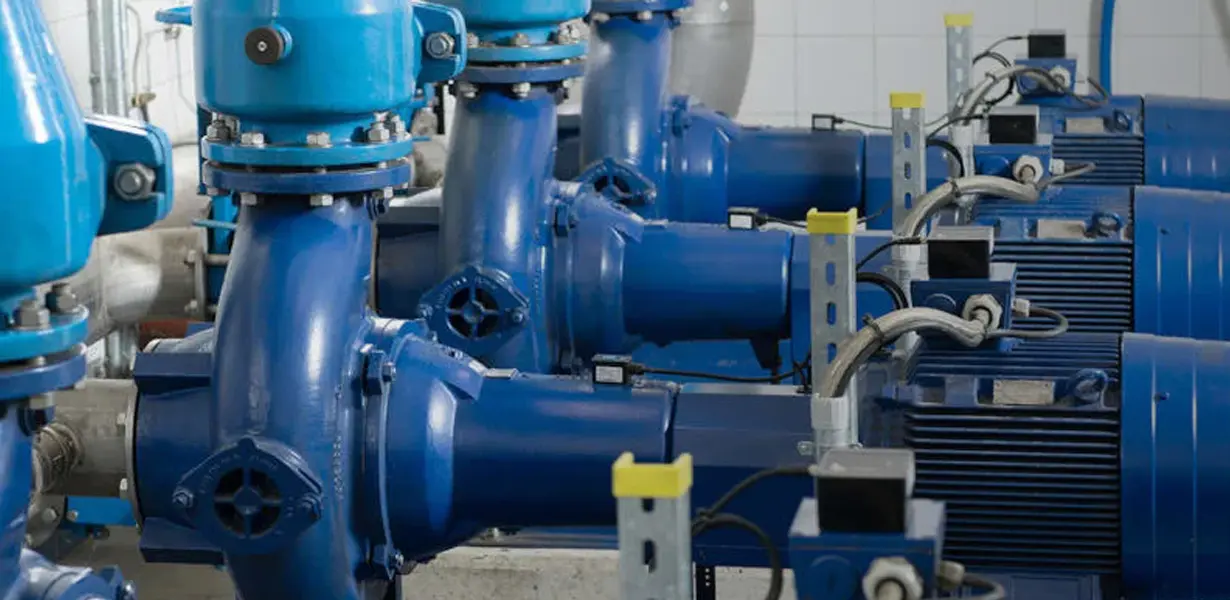
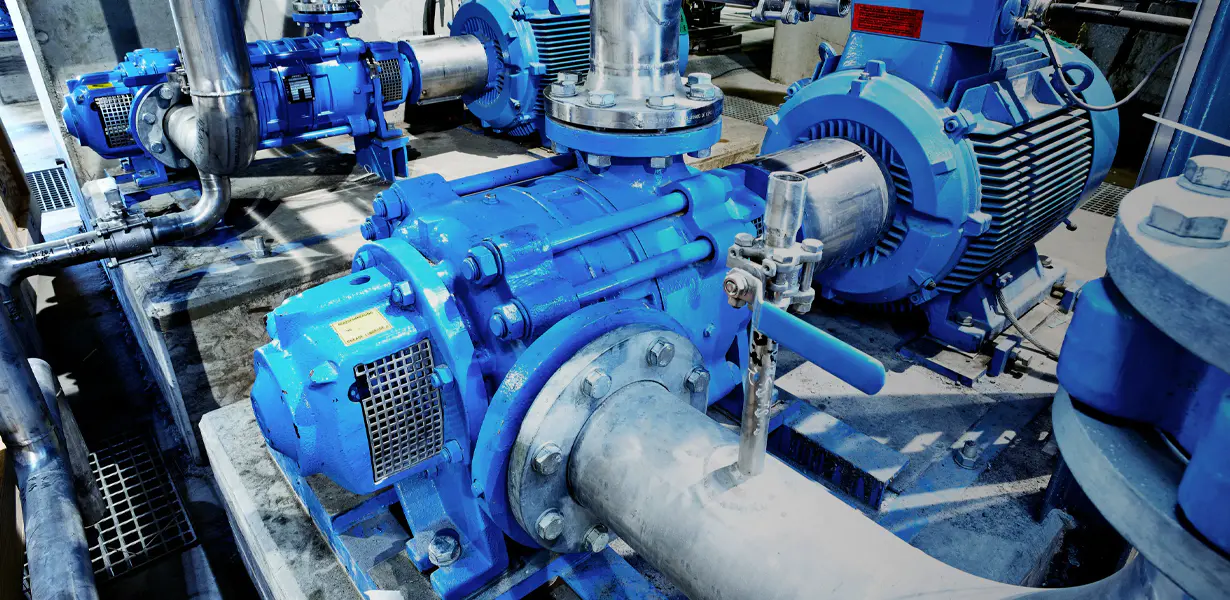
The Centrifugal Pump: A Closer Look
The centrifugal pump operates on a simple, yet highly effective principle: the conversion of rotational kinetic energy, typically from a motor or engine, into the hydrodynamic energy of the fluid flow. Its primary components include:
-
Impeller: This is the rotating component with vanes that imparts velocity to the water.
-
Casing (Volute or Diffuser): This stationary housing collects the water discharged by the impeller and directs it towards the discharge outlet. The design of the casing helps convert the velocity energy into pressure energy.
When the impeller spins, water entering the eye of the impeller is thrown outwards by centrifugal force. This creates a low-pressure area at the eye, drawing in more water, while the high-pressure water at the impeller's periphery is forced into the casing and out the discharge.
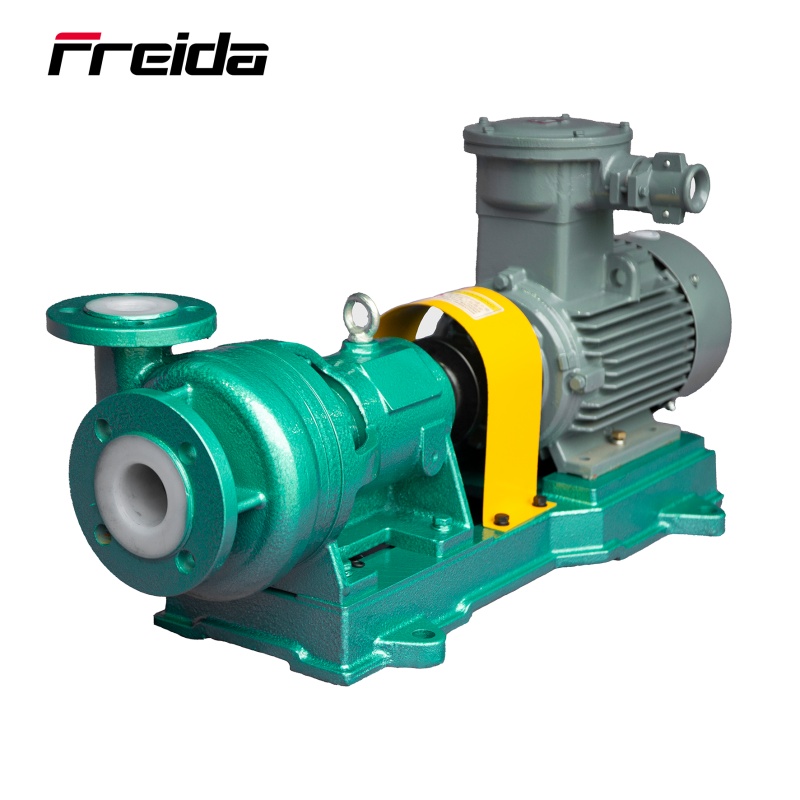

Centrifugal water pumps are ubiquitous due to their efficiency, reliability, and ability to handle high flow rates. They are found in a vast array of applications, from residential well systems and irrigation to industrial processes, municipal water supply, and HVAC systems.
Key Differentiators and Applications
The choice between a centrifugal pump and another type of water pump depends heavily on the specific application requirements, including:
-
Flow Rate and Pressure: Centrifugal pumps are generally preferred for high-flow, moderate-pressure applications.
-
Fluid Viscosity: They are most efficient with low-viscosity fluids like water.
-
Solids Handling: While some centrifugal pumps are designed for solids, positive displacement pumps might be better suited for fluids with high solid content.
-
Efficiency: Centrifugal pumps are highly efficient at their design point, but their efficiency can drop off rapidly if operated far from this point.
In conclusion, while "water pump" is a broad umbrella term, the centrifugal pump represents a highly versatile and widely adopted technology for moving water, distinguished by its unique operating principle and wide range of applications.






 English
English русский
русский Español
Español Français
Français












