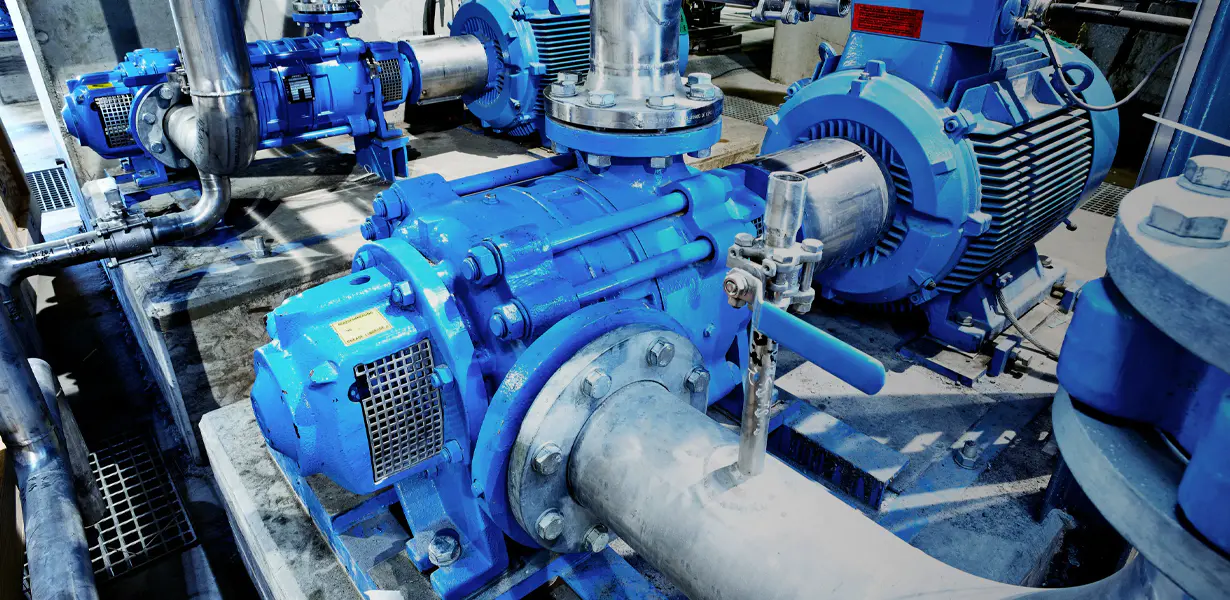
A centrifugal water pump is a ubiquitous and essential piece of machinery, playing a critical role in everything from municipal water supply systems to industrial fluid handling and residential irrigation. At its core, this device operates on a simple, yet powerful, principle: converting rotational kinetic energy into the hydrodynamic energy of fluid flow.
The Working Principle
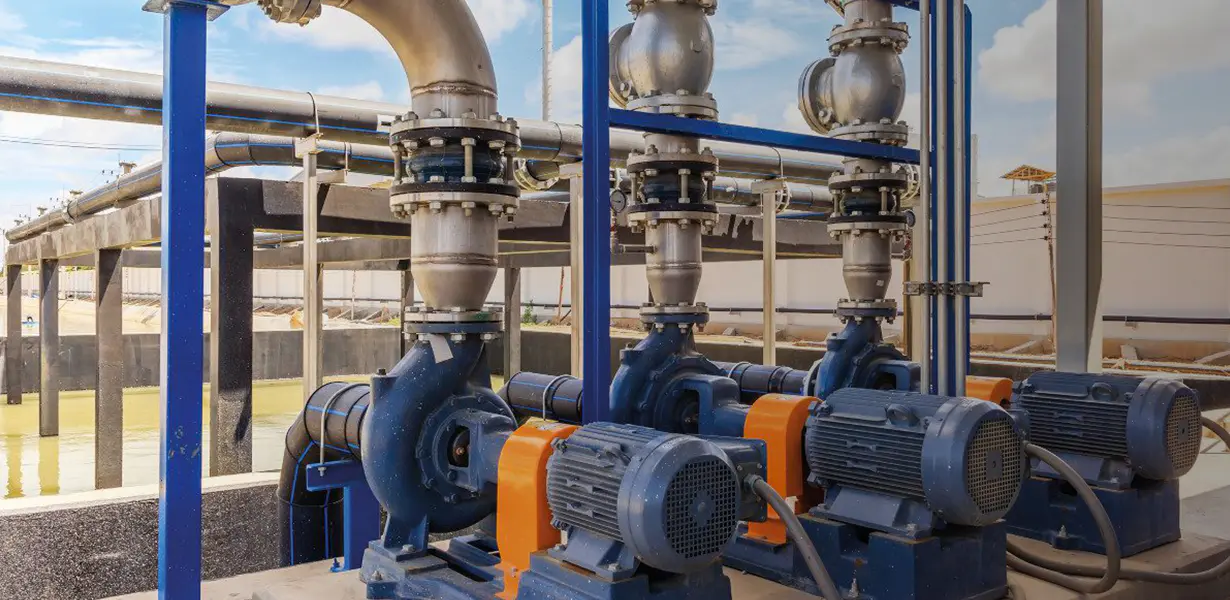
The operation of a centrifugal pump is a fascinating example of applied physics. The pump’s main components are the impeller and the casing, often called the volute. The impeller, a rotating disk with a series of curved vanes, is the heart of the pump. As the motor turns the impeller at high speeds, the fluid at the center of the impeller (the “eye”) is drawn in due to a drop in pressure.
As the fluid enters the impeller, the vanes catch the liquid and fling it outward radially. The centrifugal force exerted on the fluid increases its velocity and kinetic energy. The fluid then enters the volute, a spiral-shaped casing that surrounds the impeller. The volute’s design is crucial; its cross-sectional area increases toward the discharge outlet. This increase in area causes the high-velocity fluid to slow down, converting its kinetic energy into static pressure energy. This high-pressure fluid is then discharged from the pump.
Key Components
Beyond the impeller and casing, a few other components are vital for the efficient and safe operation of a centrifugal water pump:
- Shaft: Connects the motor to the impeller, transmitting rotational power.
- Shaft Seal: Prevents fluid leakage from the casing along the shaft. Mechanical seals are most common, offering a reliable barrier.
- Bearings: Support the shaft and impeller, ensuring smooth, low-friction rotation.
- Suction and Discharge Nozzles: The inlets and outlets for the fluid. The suction nozzle is at the eye of the impeller, and the discharge nozzle is at the end of the volute.
Types and Applications
The versatility of the centrifugal pump is evident in its wide range of applications and variants:
- End Suction Pumps: The most common type, with a single impeller and an inlet on one side. Used for general water transfer, irrigation, and HVAC systems.
- Double Suction Pumps: Designed for high flow rates, these pumps have an impeller that draws fluid from both sides, which balances axial thrust and increases efficiency. They are often found in large-scale municipal waterworks.
- Multistage Pumps: These pumps contain two or more impellers in series. Each stage boosts the fluid pressure, making them ideal for high-head applications like boiler feed systems, pressure boosting, and reverse osmosis.
- Submersible Pumps: Hermetically sealed with a motor and pump in a single unit, these pumps are designed to be fully submerged in the fluid. They are used for dewatering, well water extraction, and wastewater management.

Advantages and Limitations
A centrifugal water pump offers several distinct advantages:
- Simple Design: Fewer moving parts means easier maintenance and higher reliability.
- Smooth Flow: The continuous, non-pulsating flow is ideal for many industrial processes.
- High Efficiency: They are highly efficient for handling low-viscosity fluids at high flow rates.
- Versatility: They can be adapted for a wide range of fluids, from clean water to slurries.
However, they also have limitations. They are generally not suitable for very high-viscosity fluids and can be inefficient at low flow rates. They also require priming—the casing must be filled with liquid before operation to create the necessary suction pressure.
In conclusion, the centrifugal water pump is a cornerstone of modern infrastructure. Its robust design and effective operation have made it the go-to solution for countless fluid transfer challenges, and its role in our daily lives, though often unseen, is undeniably critical.






 English
English русский
русский Español
Español Français
Français












