Chemical pumps are specialized devices designed to transport corrosive, abrasive, or high-temperature fluids. They are widely used in various industries, including petrochemicals, fine chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and environmental protection. Due to the unique nature of the fluids they handle, chemical pumps differ significantly from standard water pumps in their materials, structure, and sealing methods. Understanding the different types of chemical pumps is crucial for selecting the right equipment to ensure the safety and efficiency of production processes.
1. Centrifugal Chemical Pumps
Centrifugal pumps are the most common type of pump in the chemical industry. They work by using the centrifugal force generated by a rotating impeller to move liquid. Based on their structure and application, centrifugal chemical pumps can be further categorized:
-
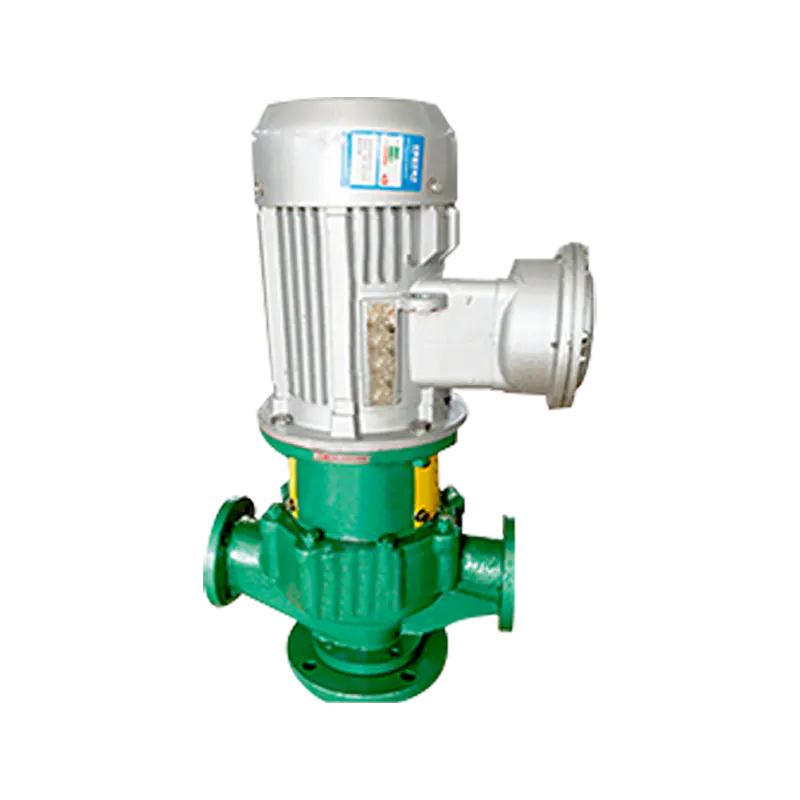
Horizontal Single-Stage Single-Suction Chemical Centrifugal Pump: This is the most prevalent type, known for its simple structure and easy maintenance. It is typically used for transporting clean liquids without solid particles. The pump body and impeller are usually made from corrosion-resistant materials, such as stainless steel or fluoroplastics.
-
Vertical Long-Shaft Sump Pump: The pump body of this type is submerged in the liquid, while the motor is mounted above the liquid surface. It is suitable for pumping liquids containing solids or those that require hermetic transport, especially when pumping from the bottom of tanks.
-
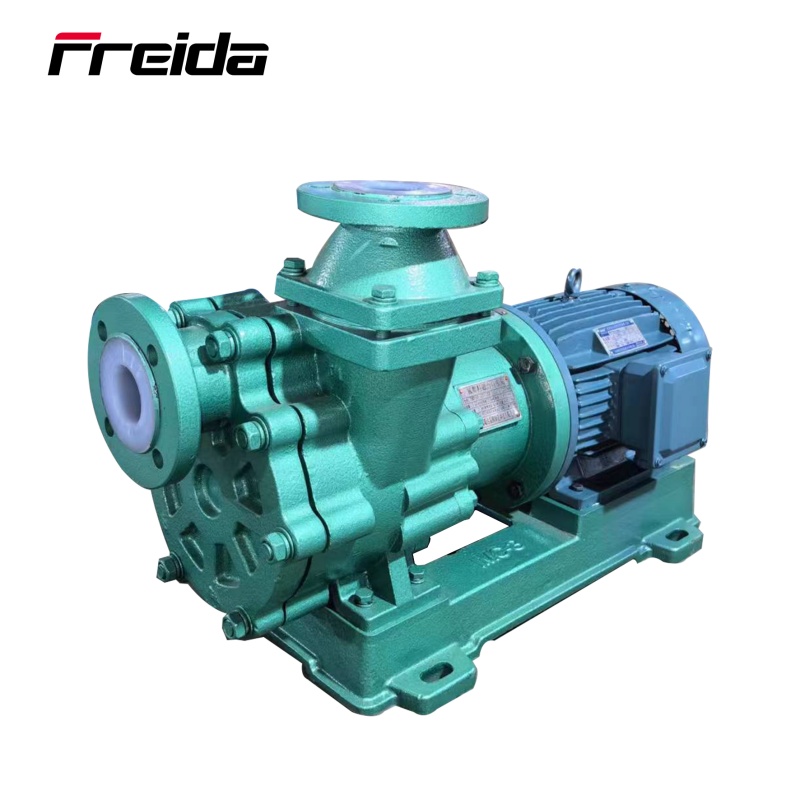
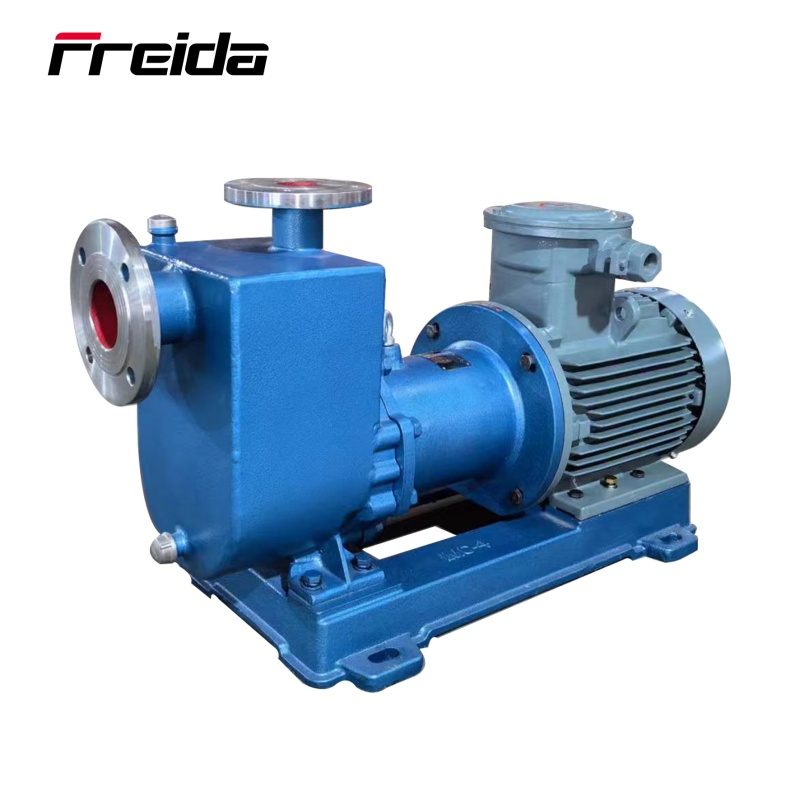
Self-Priming Chemical Centrifugal Pump: This pump does not require pre-filling with liquid before starting. It can automatically expel air from the suction pipe to achieve self-priming. It is ideal for applications where the pump needs to operate without a flooded suction line, such as pumping from underground storage tanks.
2. Magnetic Drive Pumps
Also known as mag-drive pumps or canned motor pumps, magnetic drive pumps are a type of leak-free chemical pump. Their key feature is the use of a magnetic coupling to transmit torque instead of a traditional mechanical seal.
-
How They Work: The rotor of the electric motor is non-contact connected to the pump impeller's rotor through external and internal magnets. As the motor turns, the external magnets drive the internal magnets and impeller to rotate in sync, thereby pumping the liquid.
-
Advantages: Their biggest advantage is being completely leak-free, eliminating any leakage issues caused by wear or failure of mechanical seals. They are especially suitable for handling highly toxic, flammable, explosive, or strong corrosive media.
-
Disadvantages: They are relatively more expensive and are not suitable for pumping liquids containing solid particles, as these particles can cause dry friction damage to the slide bearings.
3. Diaphragm Pumps
Diaphragm pumps are a type of positive displacement pump. They work by using the reciprocating motion of a diaphragm to change the volume of the pump chamber, thereby drawing in and expelling liquid.
-
How They Work: A diaphragm, driven by an electric motor, air, or hydraulics, moves back and forth. When the diaphragm moves back, the pump chamber volume increases, creating a vacuum that draws in liquid. When it moves forward, the volume decreases, expelling the liquid.
-
Advantages: They have no mechanical seals, which prevents leaks. They are particularly effective for pumping liquids with solid particles, high viscosity, or strong corrosive properties.
-
Types: The main types are air-operated diaphragm pumps and electric diaphragm pumps. Air-operated versions are often used in explosion-proof environments.
4. Gear Pumps
Gear pumps are another type of positive displacement pump that uses the meshing of gears to move liquid.
-
How They Work: A pair of meshing gears rotates inside the pump casing. As the gears unmesh, a vacuum is created, drawing in liquid. As they mesh again, the liquid is squeezed out.
-
Advantages: They have a compact structure and stable flow, making them suitable for pumping high-viscosity liquids with some lubricating properties.
-
Applications: In the chemical industry, chemical gear pumps are often used for transporting high-viscosity liquids such as oils and polymers.
5. Peristaltic Pumps
Peristaltic pumps, also known as hose pumps, are a unique type of positive displacement pump.
-
How They Work: A rotor with rollers or shoes inside the pump head squeezes a flexible tube, creating a peristaltic motion that pushes the fluid forward.
-
Advantages: The fluid only comes into contact with the inner wall of the tube, not the pump body or any mechanical components. This makes them completely contamination-free. The tube is also easy to replace for cleaning or changing different media. They are suitable for pumping high-purity or shear-sensitive liquids.
-
Applications: Peristaltic pumps are widely used in pharmaceuticals, food processing, and laboratories where high hygiene standards are required.
How to Choose the Right Chemical Pump?
When selecting a chemical pump, it's essential to consider several factors:
-
Fluid properties: This includes the fluid's corrosiveness, viscosity, temperature, and whether it contains solid particles.
-
Flow rate and head: These parameters are determined by the process requirements.
-
Operating environment: Is an explosion-proof design needed? Does the fluid require hermetic transport?
-
Cost: Consider the purchasing cost, operating expenses, and maintenance costs of the pump.
By thoroughly evaluating these factors, you can select the most suitable chemical pump for your production needs, ensuring a safe, stable, and efficient process.






 English
English русский
русский Español
Español Français
Français











